By expert.
BRIDGE
A bridge is a structure built to span physical obstacles such as a body of water, valley, or road, and it typically consists of several key components. Here are the main components of a bridge:
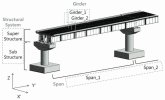
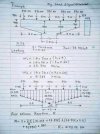
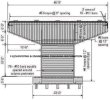
## 1. Deck
- Description: The surface of the bridge that carries the traffic (vehicles, pedestrians, trains, etc.). The deck is usually made of concrete, steel, or wood.
- Function: Provides a stable surface for the movement of traffic.
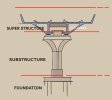
## 2. Superstructure
- Description: The part of the bridge that supports the deck and includes components like girders, beams, trusses, or arches.
- Function: Transfers the load from the deck to the substructure.
## 3. Substructure
- Description: The part of the bridge that supports the superstructure and transfers loads to the foundation.
- Components:
- Piers: Vertical supports between the ends of a bridge span.
- Abutments: Structures at the ends of the bridge that support the deck and connect it to the ground.
- Function: Provides stability to the bridge by anchoring it to the ground.
## 4. Foundation
- Description: The base of the bridge that is anchored deep into the ground to support the entire structure.
- Types:
- Shallow Foundations: Used when the soil near the surface is strong enough to support the bridge.
- Deep Foundations (Piles): Used when the surface soil is weak, requiring deeper anchorage.
- Function: Transfers the loads from the bridge to the ground.
## 5. Bearings
- Description: Devices placed between the superstructure and the substructure.
- Types: Elastomeric, sliding, or roller bearings.
- Function: Allow controlled movement of the bridge (due to expansion, contraction, or loads) while reducing stresses on the bridge components.
## 6. Expansion Joints
- Description: Gaps placed in the bridge deck to allow for thermal expansion and contraction.
- Function: Prevents damage to the bridge due to temperature changes or other movements.
## 7. Parapets/Railings
- Description: Safety barriers installed along the edges of the bridge deck.
- Function: Protects vehicles and pedestrians from falling off the bridge.
## 8. Approach Slab
- Description: The transition section between the roadway and the bridge deck.
- Function: Provides a smooth transition onto the bridge and reduces settlement problems at the ends of the bridge.
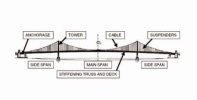
## 9. Cables (in cable-stayed or suspension bridges)
- Description: High-strength steel cables used to support the deck in cable-stayed or suspension bridges.
- Function: Distribute the weight of the deck and transfer it to the towers or pylons.
## 10. Towers or Pylons (in cable-stayed or suspension bridges)
- Description: Tall vertical structures that support the cables in cable-stayed or suspension bridges.
- Function: Provide height and support to the cables, allowing the bridge to span large distances.
These components work together to ensure the bridge is stable, durable, and safe for use.